

Ureter is the tubular tissue that connects the kidney to the urinary bladder.
An ectopic ureter is an abnormality of the ureter where the ureter does not enter into the urinary bladder in the correct anatomic position.
Ectopic ureters are the most common congenital cause of urinary incontinence in dogs. Ectopic ureter is thought to occur because of disruption in normal embryogenesis and is commonly associated with other abnormalities of the urogenital tract.
Sign and symptoms include continuous or intermittent urinary incontinence, urine leakage when lying down and/or sleeping.
Although ectopic ureter is reportedly a rare condition in dogs, it is the most common congenital cause of urinary incontinence.
The disease is thought to arise because of disruption in normal embryogenesis and is commonly associated with other anomalies within the urogenital tract.
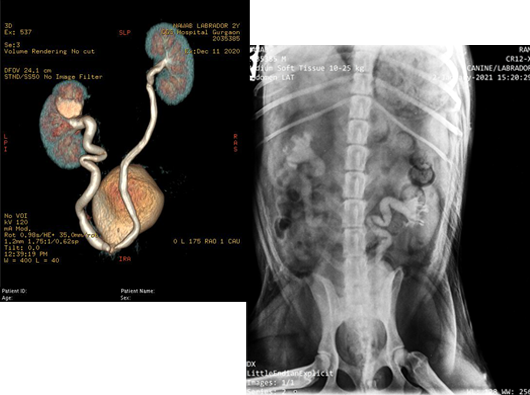
A three year old male Labrador retriever was presented with history of dribbling of urine and left renal hydronephrosis. Contrast CT-scan of the abdomen was done which revealed bilateral ectopic ureter. Bilateral ectopic ureter re-implantation surgery was performed. Post surgery contrast radiograph and CT scan revealed normal positioning of the ureters within the bladder.